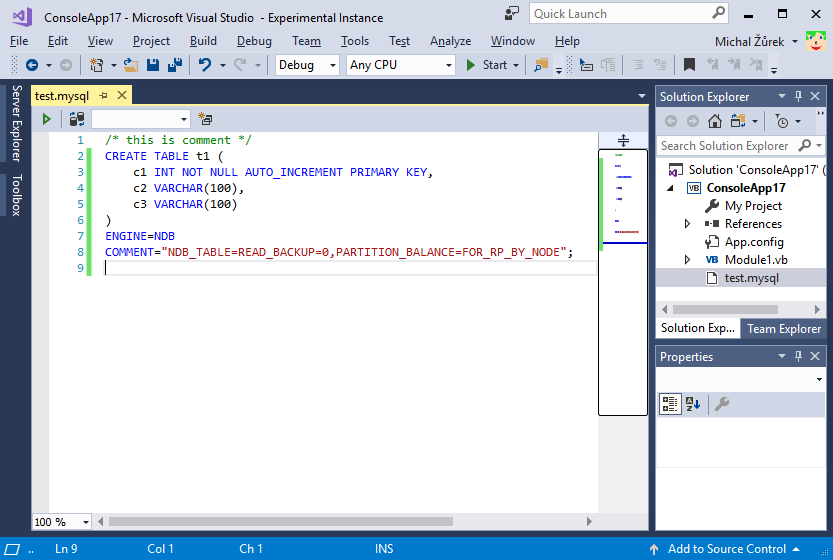
Mysql Visual Studio Code
This section describes how to create a new connection with or without encryption. After a connection is successfully established, all settings are saved for future use. When you start Visual Studio for the next time, open the connection node in Server Explorer to establish a connection to the MySQL server again. The instructions for setting up connections are provided in these sections.
To modify or delete a connection, start MySQL Connections Manager and select an existing connection. You can modify any of the settings by overwriting the existing values with new ones. The connection may be modified or deleted only if no active editor for its objects is opened; otherwise, you may lose your data.
The 'Working with MySQL' Lesson is part of the full, Visual Studio Code Can Do That? Course featured in this preview video. Here's what you'd learn in this lesson: Burke shows how to connect to a MySQL database located in a docker container using VS Code. Connect mysql to visual studio 2019connect mysql to VS19.
Mysql Connector Python Visual Studio Code
To create a connection to an existing MySQL database:
Click in the Server Explorer menu bar to open the MySQL Connections Manager window.
Click to create a new connection.
Provide a unique name for the new connection in the required Connection Name field.
Confirm that
TCP/IP (standard)is selected as the connection method.In the Parameters tab, add or modify the following information:
Hostname: and Port:
The name (or IP address) and port number of the computer hosting the MySQL server. For example,
localhostif the MySQL server is installed on the local computer. The default port value is 3306.Username:
The name of a valid MySQL user account.
Password:
The password of the user account specified previously.
Default Schema:
A default schema name is required to open the connection. Select a name from the list.
Click to verify the connection information.
Click to create and store the new connection. The new connection now appears in MySQL Connections Manager. Optionally, select the new connection from Connections Manager to add its tables, views, stored procedures, stored functions, and UDFs to the Data Connections node in Server Explorer.

X Protocol connections can be configured to use SSL with PEM or PFX files. Connections must be created using the MySQL Connections Manager, which is supported by MySQL for Visual Studio 2.0.5 (or higher). MySQL Workbench provides similar support to add PEM files, but it does not support certificates in PFX format.
X Plugin must be installed to support connections using X Protocol (see Setting Up MySQL as a Document Store ).
In contrast, classic MySQL protocol connections support SSL PFX files only when you use MySQL Connections Manager to configure the connection.
To create a connection to a MySQL database using SSL encryption:
Click in the Server Explorer menu bar to open the MySQL Connections Manager window.
Add and test a new basic connection (see Basic Connections with MySQL Connections Manager) or double-click an existing connection to modify it.
In the SSL tab, add a path to the SSL CA, SSL CERT, and SSL Key files within the SSL PEM area. Click to verify the connection information. The next figure shows an example of SSL PEM values within this tab.
Figure 4.1 MySQL Server Connection SSL Tab
To configure SSL PFX (PKCS#12 format), select either the file-based or store-based option. Use the
.pfxfile extension to enable the correct certificate format.Click to save the connection and return to the MySQL Connections Manager window.
You must close and then reopen MySQL Connections Manager to apply the default schema.
Double-click the new SSL connection to add it to Server Explorer (or select the connection and click ). To open the JavaScript or Python code editor, right-click the connection in Server Explorer and then select an editor.
Transcript from the 'Working with MySQL' Lesson
[00:00:00]
>> Burke Holland: So let's look at MySQL here. We have an extension that I've included called MySQL. And then inside of that, I've already connected, let's disconnect.
>> Burke Holland: No, let's not do that, Escape. Let me just disconnect this one, and we'll start from scratch. So let's add a new connection.
[00:00:17] And the host name of this, you can probably guess is, what? What do you think the host name is?
>> Student: MySQL.
>> Burke Holland: MySQL, that's it, because that's the name of the container and we're linked, so we just say MySQL. So we'll say MySQL. And then it wants to know the user.
[00:00:37] In MySQL, root is the user. And then for the password, you wouldn't know this without looking in the compose file but it's right there. So we'll say example, the port we can leave as the default. I don't even know what this is, I just press enter. And then, here's our mysql database.
Connect Mysql Visual Studio Code
[00:01:00] So again, we can run queries here just like we would against SQL. So I'm going to say new query, and let's just do select * from Colors. And I think you have to end mysql statements in a semicolon. And then we'll say, mysql, run mysql query, boom. So, depending on what your database is, there's more than likely an extension for it inside of the S code so that you can work with your data and your databases without leaving your editor, which is a pretty cool thing.
